Security, IAM & Secrets
This page describes how TLS, IAM roles and secrets are used to protect the services managed by this repository. It corresponds to the Security & Secrets diagram and focuses on the infra view rather than application logic.
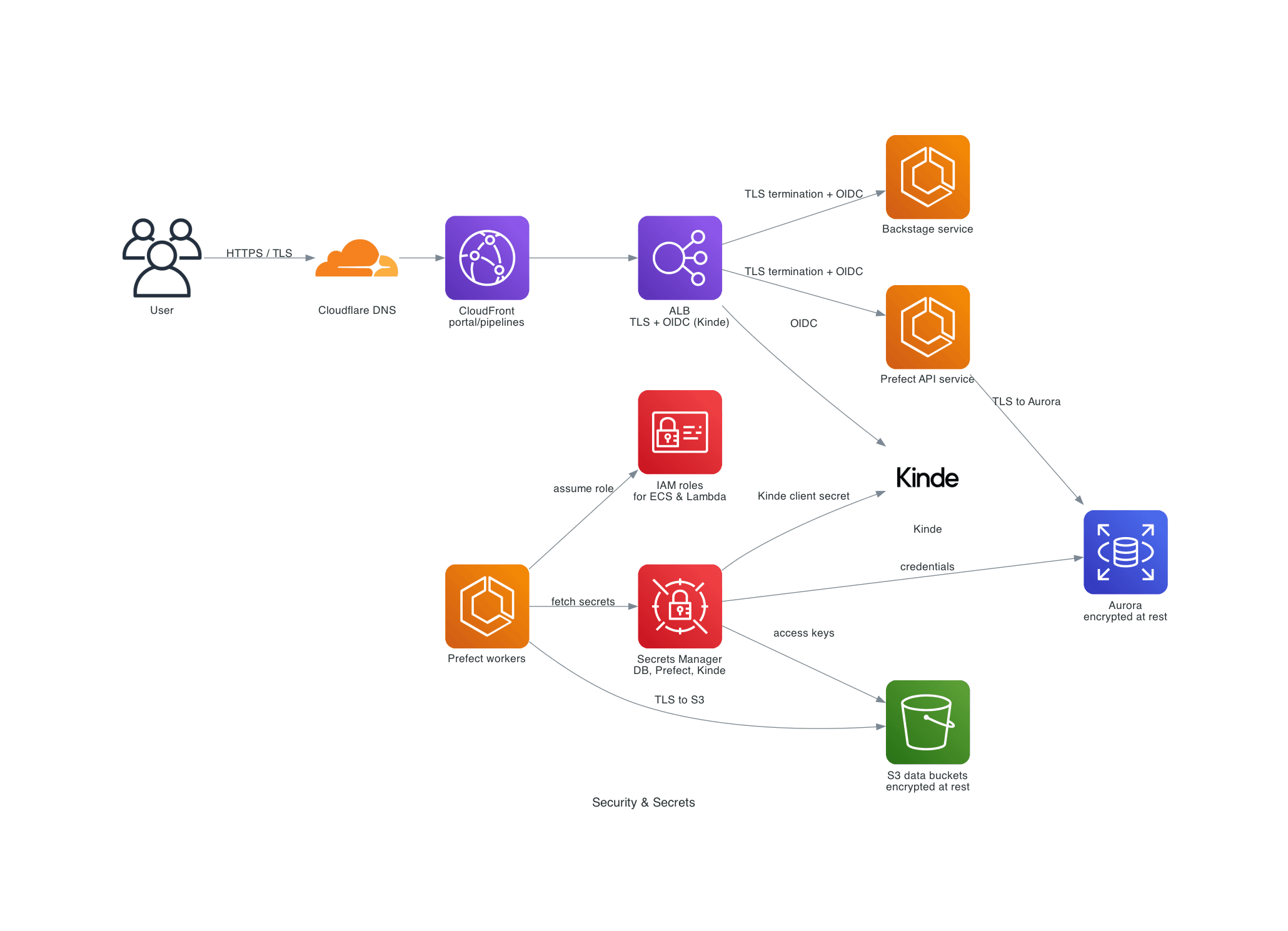
The main concerns are:
- TLS termination and OIDC authentication at the Application Load Balancer
- IAM roles and policies for ECS tasks and Lambda functions
- Secrets stored in AWS Secrets Manager (and related parameters) for Kinde, databases and other external services
TLS and entry-point security (overview)
From a networking point of view (see also Networking & Entry Points):
- Cloudflare serves DNS for
rocketclub.onlineand proxies traffic towards AWS. - CloudFront distributions front the Application Load Balancer for
portal.rocketclub.onlineandpipelines.rocketclub.online. - The ALB terminates HTTPS/TLS and performs OIDC authentication with Kinde before routing traffic to ECS services for Backstage and Prefect.
TLS certificates for the ALB origin are managed via the acm-alb-origin module, and ALB resources, listeners and listener rules live under infra/platform/infra/modules/core/alb.
IAM roles and policies
IAM configuration for the core services is managed in the infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam module and applied in infra/platform/infra/envs/prod.
At a high level:
- ECS tasks for Backstage and Prefect have task roles that allow them to:
- Read/write from S3 data buckets provisioned in this repo
- Read application secrets from AWS Secrets Manager
- Emit logs and metrics to CloudWatch and other AWS services as needed
- Lambda functions (such as the
.orkprocessor) have execution roles that allow them to:- Read
.orkfiles from the design files bucket - Write processed data to Neo4j Aura and Cloudinary using credentials stored in Secrets Manager
- Read
- CI/CD jobs (Terraform in CircleCI) use IAM roles with permissions scoped to manage the infrastructure resources defined in this repository.
The exact policies and role names are defined in Terraform under infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam and wired into ECS and Lambda modules. This page does not attempt to document every statement; Terraform remains the source of truth.
Secrets Manager and Kinde OIDC configuration
Kinde is configured directly on the ALB using authenticate-oidc actions on HTTPS listener rules for both Backstage and Prefect:
- Listener rules live in
infra/platform/infra/modules/core/alb/listener_rules.tf. - The Kinde endpoints are derived from
var.kinde_domain(for exampleronaldhatcher.kinde.com). - The Kinde client ID comes from
var.kinde_client_id. - The Kinde client secret is stored in AWS Secrets Manager and referenced via
var.kinde_client_secret_arn.
In infra/platform/infra/envs/prod:
infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/variables.tfdefines:kinde_domainkinde_client_idkinde_client_secret_name(the Secrets Manager name/path)
infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tfbuilds the fulllocal.kinde_client_secret_arnfrom that name, region and account ID and passes it into the ALB module.
The ALB module then uses data.aws_secretsmanager_secret_version.kinde_client_secret in infra/platform/infra/modules/core/alb/security.tf to resolve the client secret at apply time.
Other application credentials (for example database passwords, Prefect tokens, Cloudinary and Neo4j credentials) are also stored in AWS Secrets Manager and consumed by ECS tasks and Lambda functions via IAM roles defined in the iam module.
Secrets and parameters follow these conventions:
- Secrets Manager paths are typically
${environment}/service/thing, for exampleprod/backstage/database-url. - SSM Parameter Store paths are typically
/${environment}/namespace/resource, for example/prod/blog-data/buckets/cache.
Where this page shows prod/..., replace prod with the appropriate environment name for non-prod environments.
Key secrets in AWS Secrets Manager
The table below lists the main Secrets Manager entries that application and infra code are expected to use directly. It is not a complete inventory; Terraform remains the source of truth.
| Secret name (prod) | Purpose | Primary consumers | Owned/defined by |
|---|---|---|---|
prod/db/admin | Aurora admin credentials (JSON username / password) | Aurora cluster (master_username / master_password); Backstage DB bootstrap/inspect tasks (DB_ADMIN_SECRET_JSON) | Terraform: infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam, infra/platform/infra/modules/core/aurora |
prod/backstage/db | Backstage DB username/password (JSON) | Backstage DB bootstrap task (BACKSTAGE_DB_SECRET_JSON) | Terraform: infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam; consumed by infra/platform/infra/modules/apps/backstage |
prod/backstage/database-url | Backstage database connection URL (PostgreSQL) | Backstage ECS task container (BACKSTAGE_DATABASE_URL env var) | Secret container defined in infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam; value set in infra/platform/infra/envs/prod |
prod/backstage/session-secret | Backstage auth session secret | Backstage ECS task container (AUTH_SESSION_SECRET env var) | Terraform: infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam; consumed by infra/platform/infra/modules/apps/backstage |
prod/github/pat/blog_data_ci | Shared GitHub PAT for Backstage catalog discovery and Prefect deployer | Backstage backend (GITHUB_TOKEN env var); Prefect deployer ECS task | External secret in AWS Secrets Manager; value managed manually (not stored in Terraform state) |
prod/circleci/pat/backstage | CircleCI PAT used by the Backstage backend | Backstage ECS task container (CIRCLECI_AUTH_TOKEN env var) | External secret in AWS Secrets Manager; value managed manually (not stored in Terraform state) |
prod/prefect/database-url | Prefect database connection URL (PostgreSQL) | Prefect API ECS service container (PREFECT_API_DATABASE_CONNECTION_URL env var) | Terraform: infra/platform/infra/modules/apps/prefect-api (+ env wiring in infra/platform/infra/envs/prod) |
prod/prefect/api-auth | Prefect API authentication (for workers and CI) | Prefect workers / CI when talking to the Prefect API | Stored in AWS Secrets Manager (external / manually managed secret) |
prod/kinde/client-secret-2pS4d3 | Kinde OIDC client secret used by the ALB | ALB OIDC authentication for Backstage and Prefect | Stored in AWS Secrets Manager; referenced via kinde_client_secret_name / kinde_client_secret_arn |
blog-data/neo4j/credentials | Neo4j connection URI, username and password | Prefect flows and the blog frontend | Stored in AWS Secrets Manager; referenced by pipeline code (outside infra root) |
blog-data/cloudinary/credentials | Cloudinary cloud name, API key and secret | Prefect flows and the blog frontend | Stored in AWS Secrets Manager; referenced by pipeline code (outside infra root) |
Note: In non-prod environments, replace the
prod/prefix with the environment name (for exampledev/backstage/database-url).
Key parameters in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store (SSM)
Terraform also publishes a small set of SSM parameters that other code (CI, Prefect deployer, ALB) reads at runtime. These are the ones developers are most likely to need:
| Parameter name (prod) | Purpose / value | Primary consumers | Defined in Terraform |
|---|---|---|---|
/prod/shared/cf_alb_secret | SecureString shared secret header for CloudFront -> ALB requests | ALB + CloudFront modules (via cf_alb_secret_param_name) | infra/platform/infra/modules/core/iam, infra/platform/infra/modules/core/alb, infra/platform/infra/modules/core/cloudfront-apps |
/prod/blog-data/buckets/cache | S3 bucket name for the blog-data cache layer | Prefect flows/tools | infra/platform/infra/modules/core/s3-data/ssm-parameters.tf |
/prod/blog-data/buckets/raw | S3 bucket name for the blog-data raw layer | Prefect flows | infra/platform/infra/modules/core/s3-data/ssm-parameters.tf |
/prod/blog-data/buckets/clean | S3 bucket name for the blog-data clean layer | Prefect flows | infra/platform/infra/modules/core/s3-data/ssm-parameters.tf |
/prod/blog-data/buckets/design-files | S3 bucket name for the design files layer | Lambda .ork processor and tooling | infra/platform/infra/modules/core/s3-data/ssm-parameters.tf |
/prod/infra/park_mode | Marker for overall infra park mode: parked / unparked | CI/Terraform workflows | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
/prod/infra/database_restore_mode | Aurora restore mode: from_final_snapshot / clean | CI/Terraform workflows (controls restore variables) | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
/prod/prefect/deployer/cluster_arn | ECS cluster ARN used by the internal Prefect deployer task | CI/scripts that trigger the Prefect deployer ECS task | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
/prod/prefect/deployer/task_definition_arn | Task definition ARN for the Prefect deployer | CI/scripts that trigger the Prefect deployer ECS task | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
/prod/prefect/deployer/subnet_ids | Comma-separated list of private subnet IDs for the deployer task | CI/scripts that trigger the Prefect deployer ECS task | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
/prod/prefect/deployer/security_group_id | Security group ID for the Prefect deployer task | CI/scripts that trigger the Prefect deployer ECS task | infra/platform/infra/envs/prod/main.tf |
Kinde OIDC runbook (config & rotation)
When you need to change or rotate Kinde credentials:
- Update Kinde app: In the Kinde dashboard, update or rotate the client secret for the application used by
portal.rocketclub.onlineandpipelines.rocketclub.online. - Update Secrets Manager: In AWS Secrets Manager, update the secret whose name is given by
var.kinde_client_secret_namewith the new client secret value. - Apply Terraform: Run a Terraform plan/apply for
infra/platform/infra/envs/prod(typically via theterraform-prodCircleCI workflow). This refreshes the ALB listener rule configuration with the new client secret. - Verify login: Hit
https://portal.rocketclub.onlineandhttps://pipelines.rocketclub.onlinein a browser and confirm Kinde login works end-to-end (no redirect loops or 403s).
If authentication starts failing in production, this section plus the ALB and Kinde logs are the starting points for debugging.